Understanding the While Loop in Programming
In the world of computer programming, loops are invaluable tools that allow us to execute a block of code repeatedly until a certain condition is met. Among these loops, the “while” loop is particularly useful when you want to perform a task repeatedly as long as a specific condition holds true.
What is a While Loop?
A while loop is a control structure in programming that repeatedly executes a block of code as long as a specified condition remains true. If the condition is false from the beginning, the loop will not execute the code at all. The loop relies on the condition being true for any code execution to occur, making it a powerful tool for scenarios where the code needs to run only under certain conditions.
Syntax of a While Loop
The syntax of a while loop is straightforward:
while (condition) {
// body of the loop
}
The loop follows a simple sequence of steps:
- Evaluation of Test Expression: The loop begins by evaluating a test expression.
- Condition Check: If the test expression is true, the code inside the loop’s body is executed.
- Re-evaluation: After executing the code, the test expression is evaluated again.
- Continuation or Termination: The process continues until the test expression becomes false, at which point the while loop terminates.
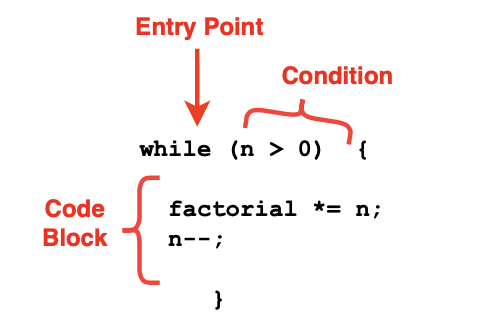
Practical Example: Calculating Factorials
A practical example of a while loop can be seen in calculating the factorial of a number. The factorial of a number ‘n’ is the product of all positive integers from 1 to ‘n’. To compute this using a while loop, you initialize a factorial variable to 1 and repeatedly multiply it by ‘n’ while decrementing ‘n’ until ‘n’ becomes 0. This ensures that you calculate the factorial correctly.
Example Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n = 5;
int factorial = 1;
while (n > 0) {
factorial *= n;
n--;
}
cout << "Factorial of 5 is: " << factorial << endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
csharpCopy codeFactorial of 5 is: 120
Importance of Termination Conditions
In algorithm design, it’s essential to define clear and well-defined termination conditions for while loops. The termination condition specifies when the loop should stop executing. Without proper termination conditions, a while loop can run indefinitely, leading to what’s known as an “infinite loop.” Infinite loops can crash programs and consume excessive system resources, making them a critical issue to avoid.
Optimizing While Loops
Optimizing while loops involves making them more efficient by minimizing unnecessary iterations. Two common optimization techniques are using loop control statements like break and continue.
Using break to Exit Early
The break statement allows you to exit the loop prematurely, even before the termination condition is met. This can be useful, for example, if you are searching for a value in an array. Once you find the value, you can break out of the loop instead of continuing to search through the remaining elements.
Using continue to Skip Iterations
The continue statement skips the current iteration of the loop and moves to the next one. This is particularly useful when you want to skip certain elements or avoid executing some code under specific conditions.
Example Code with break and continue:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int numbers[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
int target = 6;
// Using 'break' to exit the loop early when the target is found
for (int num : numbers) {
if (num == target) {
cout << "Target found: " << target << endl;
break; // Exit the loop immediately
}
cout << "Checking: " << num << endl;
}
// Using 'continue' to skip specific elements
for (int num : numbers) {
if (num % 2 == 0) {
continue; // Skip even numbers
}
cout << "Odd number: " << num << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Output:
yamlCopy codeChecking: 1
Checking: 2
Checking: 3
Checking: 4
Checking: 5
Target found: 6
Odd number: 1
Odd number: 3
Odd number: 5
Odd number: 7
Odd number: 9
In this example:
- The first loop uses
breakto exit the loop immediately when the target value is found, preventing unnecessary iterations. - The second loop uses
continueto skip even numbers, so only odd numbers are printed, avoiding the execution of code for even numbers.
Conclusion
The while loop is a powerful tool in programming, providing a way to execute a block of code repeatedly as long as a specified condition is true. By understanding and properly using while loops, along with optimization techniques like break and continue, you can write efficient and effective code. Ensuring that your while loops have clear termination conditions is crucial to prevent infinite loops and ensure your programs run smoothly.